by Rachel Lowe
Are sunburns part of your summer routine?
Summer is here and once you again you look like a hot red tomato within two hours! All your friends have their tan on, while you eagerly reach over for your shades and a sweater to cover up that nasty red burn on your pale skin. Can you relate to this? Get the details you need to know in order to prevent this from ever happening again.
Our Skin Layers and tanning ability
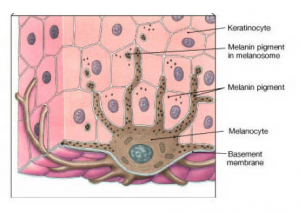
Our skin is the largest organ in our body. It consists of 3 layers; epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis. The epidermis is the outermost layer, which includes hair, nails, and sweat glands. Within this outer layer there are keratinocyte cells, where melanocyte produce melanin.
Melanin is the pigment that gives you your skin tone. It is your own body’s natural way to protect itself from the UV rays of the sun. The more sunlight exposure you receive, the more melanocyte cells produce melanin. Since melanocytes lie in the deepest layer of the epidermis, when exposed to sunlight, we get the production of two different types of melanin; eumelanin and phenomelanin. The more eumelanin you produce, the darker your skin becomes. If you have more phenomelanin, you produce freckles rather than get tanned. Once melanosomes are filled with melanin, they extend in between keratinocyte cells and begin to form an umbrella covering around the keratinocyte’s nucleus to protect it from the UV rays.
Although sunlight exposure plays a factor in the amount of melanin produced, everyone has the same number of melanocytes in their body. The difference one’s tanning ability is due to the amount of melanin produced from melanocyte cells. The more melanin produced, the more tanned you get, and studies show that you’re less likely they will be diagnosed with skin cancer in your later years.
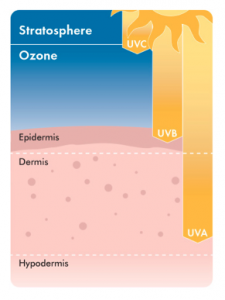
UV Rays and their effect on our skin cells
There are three types of ray exposures from the sun; UVA, UVB, and UVC. Luckily, only UVA and UVB rays reach the Earth’s atmosphere. UVC rays have the strongest wavelength, but since their wavelength is short, their rays do not enter into the Earth’s atmosphere and is absorbed by the ozone layer. UVA rays have the longest wavelength and ages us, while UVB rays make us burn. UVA rays penetrate deep into the skin’s deepest layer; the dermis, where melanocyte cells lie. When UVA rays hit the dermis, it damages the DNA of the melanocytes making it difficult for them to produce melanin, and to repair itself. When this happens, the skin’s natural body defense is down, and is more susceptible to skin cancer. In comparison, UVB rays penetrate only the superficial layers of the epidermis, and similar to UVA rays, they damage the DNA of cells. Therefore, regardless of the skin type you have, sunscreen is needed to protect the sun from its rays.
Sunscreen and SPF
Sun Protective Factor (SPF) is the percentage of UVB rays that are blocked. Since UVB rays penetrate the epidermis of the skin and can cause sunburns, it is recommended that everyone above the age of 6 months of age put on sunscreen. Children under the age of 6 months should not be going out into the sun out into the sun because their skin is still very sensitive.
Although the common levels of SPF are SPF 15, 30, and 60, this does not mean that the percent of UVB ray blockage doubles as the SPF levels increase. In fact, as the SPF levels increase, the smaller of a percentage difference there is in UVB protection.
- Think of SPF in percentages.
– Approximately 93 percent of UVB rays are blocked from SPF 15.
– Approximately 97 percent of UVB rays are blocked from SPF 30.
– Approximately 98 percent of UVB rays are blocked from SPF 50.
Individuals who can easily burn or have a family history of skin cancer are recommended to wear a higher SPF and avoid over exposure to the sun. The Skin Cancer Foundation continues to recommended the wearing of sunscreen even on cloudy days because UVB rays still penetrate through the clouds into the skin.
You may be thinking that wearing a high SPF sunscreen is the key to being free from sunburns, but what about UVA rays that cause wrinkles? If protecting the look of your skin is important to you, simply choose a sunscreen that is labelled as a broad spectrum sunscreen. This sunscreen contains zinc oxide or titanium dioxide which will blocks UVA rays.
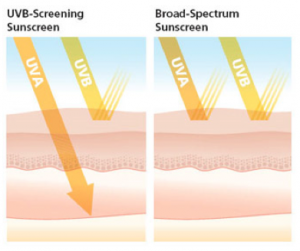
Whether you are a fan of sunscreen or not, it is important to be aware and protected. If your goal is to prevent painful sunburns and prevent wrinkles, a combination of sunscreen and being smart about sun exposure (covering up, staying in the shade during the mid day and slowly allowing your body to adapt to sun exposure throughout the summer) are key factors to healthy, youthful skin!